|
|
| (895 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| ==Anchors, ultimatums and randomization==
| |
|
| |
|
| William Poundstone writes wonderful, interesting books, veritable page turners. Some of his previous works were reviewed in Chance News
| |
|
| |
|
| [http://test.causeweb.org/wiki/chance/index.php/Chance_News_13#Making_a_Mint here] and [http://test.causeweb.org/wiki/chance/index.php/Chance_News_43#Gaming_the_Vote here]. Because he has set such a personal high bar, his latest two books while fun to read, don’t quite match his earlier output.
| | ==Forsooth== |
|
| |
|
| His 2010 book, Priceless: The Myth of Fair Value (and How to Take Advantage of It) focuses on the concept of anchoring which [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anchoring Wikipedia] describes as
| | ==Quotations== |
| <blockquote>
| | “We know that people tend to overestimate the frequency of well-publicized, spectacular |
| A person begins with a first approximation (anchor) and then makes incremental adjustments based on additional information. These adjustments are usually insufficient, giving the initial anchor a great deal of influence over future assessments.
| | events compared with more commonplace ones; this is a well-understood phenomenon in |
| </blockquote> | | the literature of risk assessment and leads to the truism that when statistics plays folklore, |
| Thus says Poundstone, anchoring is beloved by behavioral economists, market consultants, advertisers, marketers, psychologists, attorneys and any other entities that wish to influence/fleece the unwary consumer/opponent. In essence, the public and the individual are easily manipulated by the mere mention of a number--a high number elicits high numbers and a low number brings forth low numbers. For example on page 11, if a (meaningless) random number (from a rigged spinning wheel) is 65, the participants claimed (on average) that the percentage of African nations in the U.N. is 45 percent whereas if the (meaningless) random number (from a rigged spinning wheel) is 10, the participants claimed (on average) that the percentage of African nations in the U.N. is 25 percent.
| | folklore always wins in a rout.” |
| <blockquote>
| | <div align=right>-- Donald Kennedy (former president of Stanford University), ''Academic Duty'', Harvard University Press, 1997, p.17</div> |
| In case you are wondering, the correct fraction of African U.N. member nations is 23 percent.
| |
| </blockquote> | |
| Much of the rest of the book is devoted to tales of how anchoring and its offshoots can be used to swindle the general public. He turns the famous Oscar Wilde saying
| |
| “A cynic is a man who knows the price of everything, and the value of nothing”
| |
| on its head in the sense that, just as with “value,” there is no such thing as price; for instance, price is easily manipulated by means of lowering the weight of a package while keeping the price the same as before. Another common commercial technique is to run non-special special discounts.
| |
|
| |
|
| Less well-known is the procedure supermarkets employ:
| | ---- |
| <blockquote>
| |
|
| |
|
| Shoppers open their wallets wider when moving through a store in a counterclockwise direction. On average, these shoppers spend $2 more a trip than clockwise shoppers…[Because] North Americans see shopping carts as ‘cars” to be driven to the right…By this theory, the right-handed majority finds it easier to make impulse purchases when the wall or shelf is to the right…[resulting in] markets putting their main entrance on the right of the store’s layout to encourage counterclockwise shopping
| | "Using scientific language and measurement doesn’t prevent a researcher from conducting flawed experiments and drawing wrong conclusions — especially when they confirm preconceptions." |
| </blockquote>
| |
|
| |
|
| Particularly amusing is his Chapter 27, “Menu Psych,” where he demonstrates how a restaurant menu can be designed to avoid “A diner who orders based on price” because said diner “is not a profitable diner.”
| | <div align=right>-- Blaise Agüera y Arcas, Margaret Mitchell and Alexander Todoorov, quoted in: The racist history behind facial recognition, ''New York Times'', 10 July 2019</div> |
| <blockquote> | |
|
| |
|
| The real agenda of the $110 price [of the seafood plate] is probably to induce customers to spring for the $65 Le Grand plate just to the left of it or the more modest seafood orders below it.
| | ==In progress== |
| </blockquote> | | [https://www.nytimes.com/2018/11/07/magazine/placebo-effect-medicine.html What if the Placebo Effect Isn’t a Trick?]<br> |
| This modus operandi of an absurdly overpriced option in order to induce the buyer to choose a slightly less overpriced option can be applied to many fields from handbags to stadium seats and imported wine.
| | by Gary Greenberg, ''New York Times Magazine'', 7 November 2018 |
|
| |
|
| Then there is the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ultimatum_game ultimatum game]:
| | [https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/17/opinion/pretrial-ai.html The Problems With Risk Assessment Tools]<br> |
| <blockquote> | | by Chelsea Barabas, Karthik Dinakar and Colin Doyle, ''New York Times'', 17 July 2019 |
| [T]he ultimatum game is a game often played in economic experiments in which two players interact to decide how to divide a sum of money that is given to them. The first player proposes how to divide the sum between the two players, and the second player can either accept or reject this proposal. If the second player rejects, neither player receives anything. If the second player accepts, the money is split according to the proposal. The game is played only once so that reciprocation is not an issue.
| |
| </blockquote>
| |
|
| |
|
| Obviously, the word “game” is a euphemism and particularly amusing is Poundstone’s discussion of Jack Welch’s divorce proceedings whereby Welch, the former head of GE, made an initial offer which his wife refused resulting in all the lawyers involved profiting mightily.
| | ==Hurricane Maria deaths== |
| <blockquote>
| | Laura Kapitula sent the following to the Isolated Statisticians e-mail list: |
| | |
| As negotiations dragged on, Jack was offering Jane a temporary allowance of $35,000 a month. To a woman of Jane’s sense of entitlement, that didn’t go far enough [!]. It was time for Jane to play the ultimatum game.
| |
| </blockquote>
| |
| Eventually, he blinked and
| |
| <blockquote>
| |
| | |
| By one calculation, Jane’s ultimatum had cost the couple $2.5 million a year for the rest of their lives.
| |
| </blockquote>
| |
| Poundstone’s 2014 book, Rock Breaks Scissors: A Practical Guide to Outguessing & Outwitting Almost Everybody spotlights the role randomness can play in competitive games such as the classic “rock, scissors, paper,” but also salary negotiations, computer passwords, multiple-choice tests, financial fraud, office pools, stock market investing, the Oscar pools. The chapters tend to be short with a recap at the end of each chapter.
| |
| | |
| Rock, scissors, paper is a well known betting game which exemplifies non-transitivity: A > B, B > C but C > A where the symbol “>” means dominates.
| |
| | |
| His Chapter 13, “How to Outguess Ponzi Schemes” concludes with
| |
| <blockquote>
| |
| Be suspicious when too many numbers just top a psychologically significant threshold.
| |
| </blockquote>
| |
| Although he doesn’t say so, this is reminiscent of [http://psychology.wikia.com/wiki/P-hacking p-hacking] whereby frequentists’ p-values just go under the magical .05 in order convince journal reviewers that the study should be published.
| |
| | |
| The most interesting chapter for statisticians is Chapter 11, “How to Outguess Fake Numbers.” He looks at the famous Benford Law of the leading digit which, to the surprise of many a convicted fraudster, is not a uniform distribution where each digit is equally likely and equal to 1/9. From [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benford's_law Wikipedia] the distribution of the leading digit is:
| |
|
| |
|
| | :[Why counting casualties after a hurricane is so hard]<br> |
| | :by Jo Craven McGinty, Wall Street Journal, 7 September 2018 |
|
| |
|
| | The article is subtitled: Indirect deaths—such as those caused by gaps in medication—can occur months after a storm, complicating tallies |
| | | |
| In this age of password hacking, Poundstone proposes using randomization and mnemonics to foil the hackers. For example, for the random password RPM8t4ka
| | Laura noted that |
| <blockquote>
| | :[https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/fact-checker/wp/2018/06/02/did-4645-people-die-in-hurricane-maria-nope/?utm_term=.0a5e6e48bf11 Did 4,645 people die in Hurricane Maria? Nope.]<br> |
| RPM8t4ka might become revolutions per minute, 8 track for Kathy.
| | :by Glenn Kessler, ''Washington Post'', 1 June 2018 |
| </blockquote>
| |
| | |
| Big Data is the rage these days, so his Chapter 18, “Outguessing Big Data,” is a must read. In this age of plastic, your cell phone carrier, bank, cable company, etc., know everything about you, including the likelihood that you might switch to a competitor who is about to have an alluring blitz campaign.
| |
| <blockquote>
| |
| You’ve probably gotten weird calls…The call means that an algorithm has predicted that you are likely to “churn” (cancel your service)…you’ll be presented with the so-called primary offer…Never accept a primary offer. Once you reject it, the caller will bring up the secondary offer. It’s all in the script. Sometimes the second offer is better; other times it’s just different…You can always reverse yourself and ask for the first after hearing the second. A still better strategy is to reject all offers. Wait a few days and then call to cancel the service. (Do this even if you intend to keep it).
| |
| </blockquote> | |
|
| |
|
| Another technique for outguessing Big Data is to phone the large corporation via Google Voice because
| | The source of the 4645 figure is a [https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMsa1803972 NEJM article]. Point estimate, the 95% confidence interval ran from 793 to 8498. |
| <blockquote>
| |
| Your Internet phone number is likely to have less data attached to it than your main number…This time the software will see your Internet phone number, not your regular one…Companies want new customers, so they are unlikely to lump blank slate numbers in with the bad apples.
| |
| </blockquote>
| |
| ===Discussion===
| |
|
| |
|
| 1. From [http://www.theiia.org/itauditarchive/index.cfm?act=itaudit.archive&fid=95] we find
| | President Trump has asserted that the actual number is |
| | [https://twitter.com/realDonaldTrump/status/1040217897703026689 6 to 18]. |
| | The ''Post'' article notes that Puerto Rican official had asked researchers at George Washington University to do an estimate of the death toll. That work is not complete. |
| | [https://prstudy.publichealth.gwu.edu/ George Washington University study] |
|
| |
|
| | :[https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/we-still-dont-know-how-many-people-died-because-of-katrina/?ex_cid=538twitter We sttill don’t know how many people died because of Katrina]<br> |
| | :by Carl Bialik, FiveThirtyEight, 26 August 2015 |
|
| |
|
| | ---- |
| | [https://www.nytimes.com/2018/09/11/climate/hurricane-evacuation-path-forecasts.html These 3 Hurricane Misconceptions Can Be Dangerous. Scientists Want to Clear Them Up.]<br> |
| | [https://journals.ametsoc.org/doi/abs/10.1175/BAMS-88-5-651 Misinterpretations of the “Cone of Uncertainty” in Florida during the 2004 Hurricane Season]<br> |
| | [https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/aboutcone.shtml Definition of the NHC Track Forecast Cone] |
| | ---- |
| | [https://www.popsci.com/moderate-drinking-benefits-risks Remember when a glass of wine a day was good for you? Here's why that changed.] |
| | ''Popular Science'', 10 September 2018 |
| | ---- |
| | [https://www.economist.com/united-states/2018/08/30/googling-the-news Googling the news]<br> |
| | ''Economist'', 1 September 2018 |
|
| |
|
| Digit First Digit
| | [https://www.cnbc.com/2018/09/17/google-tests-changes-to-its-search-algorithm-how-search-works.html We sat in on an internal Google meeting where they talked about changing the search algorithm — here's what we learned] |
| Frequency Second Digit
| | ---- |
| Frequency
| | [http://www.wyso.org/post/stats-stories-reading-writing-and-risk-literacy Reading , Writing and Risk Literacy] |
| 0 - 0.11968
| |
| 1 0.30103 0.11389
| |
| 2 0.17609 0.10882
| |
| 3 0.12494 0.10433
| |
| 4 0.09691 0.10031
| |
| 5 0.07918 0.09668
| |
| 6 0.06695 0.09337
| |
| 7 0.05799 0.09035
| |
| 8 0.05115 0.08757
| |
| 9 0.04576 0.08500
| |
|
| |
|
| Not all data sets are expected to have the digit frequencies of Benford’s Law: therefore, the guidelines for deciding whether a data set would comply are that:
| | [http://www.riskliteracy.org/] |
| * The numbers in the data set should describe the sizes of the elements in the data set.
| | ----- |
| * There should be no built-in maximum or minimum to the numbers. A maximum or minimum that occurs often would cause many numbers to have the digit patterns of the maximum or minimum.
| | [https://twitter.com/i/moments/1025000711539572737?cn=ZmxleGlibGVfcmVjc18y&refsrc=email Today is the deadliest day of the year for car wrecks in the U.S.] |
| * The numbers should not be assigned. Assigned numbers are those given to objects to identify them. Examples are social security, bank account, and telephone numbers.
| |
|
| |
|
| See [http://www.usfca.edu/fac-staff/huxleys/Benford.html] for the distribution of the first through fifth digits. Unlike the leading digit which is never a zero, these subsequent digits tend to a uniform distribution of 1/10.
| | ==Some math doodles== |
| | <math>P \left({A_1 \cup A_2}\right) = P\left({A_1}\right) + P\left({A_2}\right) -P \left({A_1 \cap A_2}\right)</math> |
|
| |
|
| 2. Poundstone’s Chapter 22, “How to Outguess the Stock Market,” is his longest chapter and perhaps the most puzzling. Here we are potentially dealing with real money, namely yours. He is enamored with the Shiller PE ratio and is quite emphatic, without the usual “the past may not be an indicator of future performance” hedge.
| | <math>P(E) = {n \choose k} p^k (1-p)^{ n-k}</math> |
| <blockquote> | |
|
| |
|
| For still better returns,…When the Shiller PE rises above 24, check the market monthly and sell whenever the market falls 6 percent or more from a recent high. Keep the proceeds in fixed income investments. Then, when Shiller PE falls below 15, check the market monthly and buy back into the market whenever the PE rises 6 percent or more from a recent low.
| | <math>\hat{p}(H|H)</math> |
| </blockquote> | |
| 3. Unfortunately, Poundstone seriously misleads when he naively cites the many behavioral economic studies which say, more or less, that the average of one (convenient) group (of university students) is different from another (convenient) group (of university students). Without referring to variability between the groups, the average difference is virtually meaningless. In addition, even if the difference is significant (statistically and practically), it is quite a leap to infer that this difference involving university students at MIT and the University of Chicago applies to all of humankind spatially and temporally.
| |
|
| |
|
| Submitted by Paul Alper
| | <math>\hat{p}(H|HH)</math> |
| | |
| ==MicroMorts==
| |
| Margaret Cibes sent a link to the following:
| |
| | |
| [http://online.wsj.com/articles/risk-is-never-a-strict-numbers-game-1405728892 Risk is never a strict numbers game]<br>
| |
| by Michael Blastland and David Spiegelhalter, ''Wall Street Journal'', 18 July 2014
| |
| | |
| Noting that people are notoriously bad at weighing risks (e.g., in preferring driving to flying), this essay explains the use ''MicroMorts'' to simplify comparisons. This unit of measure is death per million is credited to Stanford professor Ronald Howard.
| |
| | |
| David Spiegelhalter is member of the [http://understandinguncertainty.org Understanding Uncertainty] project, based at the Statistical Laboratory in the University of Cambridge.
| |
| | |
| [http://understandinguncertainty.org/node/1302 Micromorts, horses and ecstasy]
| |
| | |
| [http://understandinguncertainty.org/files/animations/Micromorts/Micromorts.html animation]
| |
| | |
| [http://plus.maths.org/content/os/issue55/features/risk/index Understanding uncertainty: Small but lethal]<br>
| |
| by David Spiegelhalter and Mike Pearson, ''Plus'' magazine, 12 July 2010
| |
|
| |
|
| ==Accidental insights== | | ==Accidental insights== |
| Line 171: |
Line 118: |
| Submitted by William Montante | | Submitted by William Montante |
|
| |
|
| ==Reproducibility==
| | ---- |
| [http://www.nytimes.com/2014/03/07/science/when-studies-are-wrong-a-coda.html?hpw&rref=science When studies are wrong: A coda]<br>
| |
| by George Johnson, ''New York Times'', 7 March 2014
| |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| Submitted by Bill Peterson
| |
| | |
| ==Finding lost aircraft==
| |
| Jeanne Albert sent a link to the following
| |
| | |
| [http://www.technologyreview.com/view/527506/how-statisticians-found-air-france-flight-447-two-years-after-it-crashed-into-atlantic/ How statisticians found Air France Flight 447 two years after it crashed into Atlantic]<br>
| |
| ''MIT Technology Review'', 27 May 2014
| |
| | |
| [http://fivethirtyeight.com/features/how-statisticians-could-help-find-flight-370/ How statisticians could help find that missing plane], by Carl Bialik, FiveThirtyEight, 17 March 2014
| |
Forsooth
Quotations
“We know that people tend to overestimate the frequency of well-publicized, spectacular
events compared with more commonplace ones; this is a well-understood phenomenon in
the literature of risk assessment and leads to the truism that when statistics plays folklore,
folklore always wins in a rout.”
-- Donald Kennedy (former president of Stanford University), Academic Duty, Harvard University Press, 1997, p.17
"Using scientific language and measurement doesn’t prevent a researcher from conducting flawed experiments and drawing wrong conclusions — especially when they confirm preconceptions."
-- Blaise Agüera y Arcas, Margaret Mitchell and Alexander Todoorov, quoted in: The racist history behind facial recognition, New York Times, 10 July 2019
In progress
What if the Placebo Effect Isn’t a Trick?
by Gary Greenberg, New York Times Magazine, 7 November 2018
The Problems With Risk Assessment Tools
by Chelsea Barabas, Karthik Dinakar and Colin Doyle, New York Times, 17 July 2019
Hurricane Maria deaths
Laura Kapitula sent the following to the Isolated Statisticians e-mail list:
- [Why counting casualties after a hurricane is so hard]
- by Jo Craven McGinty, Wall Street Journal, 7 September 2018
The article is subtitled: Indirect deaths—such as those caused by gaps in medication—can occur months after a storm, complicating tallies
Laura noted that
- Did 4,645 people die in Hurricane Maria? Nope.
- by Glenn Kessler, Washington Post, 1 June 2018
The source of the 4645 figure is a NEJM article. Point estimate, the 95% confidence interval ran from 793 to 8498.
President Trump has asserted that the actual number is
6 to 18.
The Post article notes that Puerto Rican official had asked researchers at George Washington University to do an estimate of the death toll. That work is not complete.
George Washington University study
- We sttill don’t know how many people died because of Katrina
- by Carl Bialik, FiveThirtyEight, 26 August 2015
These 3 Hurricane Misconceptions Can Be Dangerous. Scientists Want to Clear Them Up.
Misinterpretations of the “Cone of Uncertainty” in Florida during the 2004 Hurricane Season
Definition of the NHC Track Forecast Cone
Remember when a glass of wine a day was good for you? Here's why that changed.
Popular Science, 10 September 2018
Googling the news
Economist, 1 September 2018
We sat in on an internal Google meeting where they talked about changing the search algorithm — here's what we learned
Reading , Writing and Risk Literacy
[1]
Today is the deadliest day of the year for car wrecks in the U.S.
Some math doodles
<math>P \left({A_1 \cup A_2}\right) = P\left({A_1}\right) + P\left({A_2}\right) -P \left({A_1 \cap A_2}\right)</math>
<math>P(E) = {n \choose k} p^k (1-p)^{ n-k}</math>
<math>\hat{p}(H|H)</math>
<math>\hat{p}(H|HH)</math>
Accidental insights
My collective understanding of Power Laws would fit beneath the shallow end of the long tail. Curiosity, however, easily fills the fat end. I long have been intrigued by the concept and the surprisingly common appearance of power laws in varied natural, social and organizational dynamics. But, am I just seeing a statistical novelty or is there meaning and utility in Power Law relationships? Here’s a case in point.
While carrying a pair of 10 lb. hand weights one, by chance, slipped from my grasp and fell onto a piece of ceramic tile I had left on the carpeted floor. The fractured tile was inconsequential, meant for the trash.

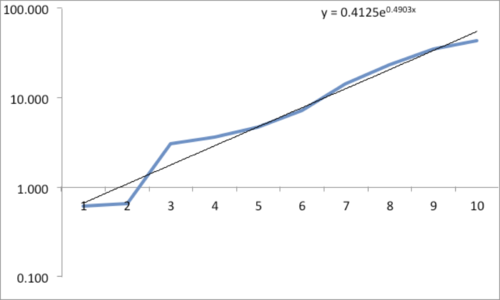
As I stared, slightly annoyed, at the mess, a favorite maxim of the Greek philosopher, Epictetus, came to mind: “On the occasion of every accident that befalls you, turn to yourself and ask what power you have to put it to use.” Could this array of large and small polygons form a Power Law? With curiosity piqued, I collected all the fragments and measured the area of each piece.
| Piece |
Sq. Inches |
% of Total
|
| 1 |
43.25 |
31.9%
|
| 2 |
35.25 |
26.0%
|
| 3 |
23.25 |
17.2%
|
| 4 |
14.10 |
10.4%
|
| 5 |
7.10 |
5.2%
|
| 6 |
4.70 |
3.5%
|
| 7 |
3.60 |
2.7%
|
| 8 |
3.03 |
2.2%
|
| 9 |
0.66 |
0.5%
|
| 10 |
0.61 |
0.5%
|
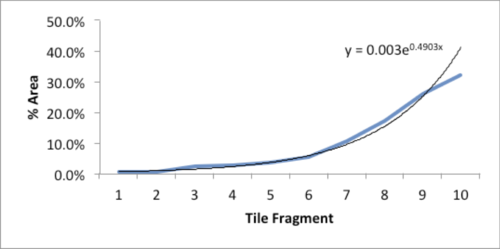
The data and plot look like a Power Law distribution. The first plot is an exponential fit of percent total area. The second plot is same data on a log normal format. Clue: Ok, data fits a straight line. I found myself again in the shallow end of the knowledge curve. Does the data reflect a Power Law or something else, and if it does what does it reflect? What insights can I gain from this accident? Favorite maxims of Epictetus and Pasteur echoed in my head:
“On the occasion of every accident that befalls you, remember to turn to yourself and inquire what power you have to turn it to use” and “Chance favors only the prepared mind.”
My “prepared” mind searched for answers, leading me down varied learning paths. Tapping the power of networks, I dropped a note to Chance News editor Bill Peterson. His quick web search surfaced a story from Nature News on research by Hans Herrmann, et. al. Shattered eggs reveal secrets of explosions. As described there, researchers have found power-law relationships for the fragments produced by shattering a pane of glass or breaking a solid object, such as a stone. Seems there is a science underpinning how things break and explode; potentially useful in Forensic reconstructions.
Bill also provided a link to a vignette from CRAN describing a maximum likelihood procedure for fitting a Power Law relationship. I am now learning my way through that.
Submitted by William Montante


